
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF UV PAINT
UV paint is a type of paint whose composition is different from today's popular paints and has a history of development of more than 50 years.
MOST COMMON MISTAKES WHEN APPLYING EPOXY
AUTOMOTIVE COATINGS MARKET
What's the Difference Between Polyurethane, Varnish, Shellac and Lacquer?
NO SELF-HEALING PAINT
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF UV PAINT
1. Overview
UV paint is a type of paint whose composition is different from today's popular paints and has a history of the development of more than 50 years.
In essence, this paint only uses the energy of UV rays to decompose the free radical initiator for the curing reaction, so it is customary to call it UV paint. This means that if any energy source is used, just enough intensity to decompose the initiator can cure the paint. Or any chemical reaction that generates free radicals also hardens the paint (like the crosslinking reaction of unsaturated polyester).
2. Some basic materials
- Oligomer: medium molecular weight compound form (lower than polymer), low viscosity, no solvents used for dilution. Usually contains acrylate radicals (with double bonds), capable of participating in the crosslinking reaction.
- Monomer: Low molecular compound, low viscosity, high evaporation temperature (the lowest is more than 90 degrees Celsius). Usually contains acrylate base such as Oligomer, used to adjust the viscosity and some features of the paint (such as adhesion, hardness, flowability, etc.)
- An optical activator: is a compound that receives UV energy, then decomposes into free radicals, thereby starting the curing reaction.
See Table 1 to see the difference in UV coating composition compared to other coating systems
Components | Solvent paint in general | UV paint |
Solids/base resin | Resin/resin (Polymer) of all kinds NC, Acrylic, epoxy, etc. | Oligomers (like Polymer but with much shorter molecular chains) contain unsaturated functional groups (usually acrylate) including types such as Polyester epoxy, urethane, etc. |
Diluent | Solvents of all kinds | Monomer (basic polymer, low viscosity, odorless or odorless) with an unsaturated functional group, usually acrylate |
Additives | Same (depending on the type of paint) |
|
Curing agent | Depending on paint system (PU, AC, NC) | Optical activator, a chemical that, when exposed to UV light, generates free radicals that combine with unsaturated radicals of oligomers and monomers to form cross-links that cure. |
Solid content | Depending on the mixing ratio of the base resin and organic solvent | Most of the ingredients are non-volatile or very little so it is considered 100%. |
Curing time | Depends on the type of paint | Immediately after UV irradiation |
Toxic | Depending on the paint system | Less harmful to the environment |
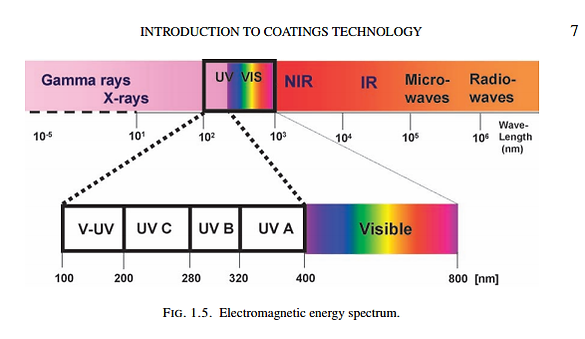
3. UV rays
UV ray is light with a wavelength in the 100-400 nm range. There are 4 types of UV rays including: UVA, UVB,UVB,UVC,V-UV (in addition, some documents also mention UV-V - Visible UV). UV rays have relatively high energy. It is this energy source that breaks the bonds of the initiating chemicals (also known as optical activators), thereby generating free radicals and initiating reactions with unsaturated bonds (usually double) available in oligomers/Monomers.
As you can see below, the UV energy of each wavelength band and the corresponding bond breaking energy)
The double bond breaking energy of C=C is present in UV light with a wavelength of 161 nm.
4. UV coating curing process
Step 1: The paint mixture including Oligomer, Monomer, PI (Photo Initiator) is applied (scanning, spraying, rolling, rolling film) to the surface of the material.
Step 2: The surface is painted under UV light, PI receives UV energy and decomposes into free radicals.
Step 3: Free radicals react with unsaturated radicals of Oligomer and Monomer, forming a cross-linking network, starting the polymerization process.
Step 4: The free radicals participate to initiate the chain reaction and react with each other, complete the curing process and the paint cures completely.
As we can see in the figure, the solid content of the UV paint remains constant throughout the curing process. Due to the crosslinking reaction, there is still shrinkage, but not significantly.
Currently, Mega Vietnam General Trading Co., Ltd. has been widely deploying raw materials for the production of UV paints, Oligomer epoxy acrylate resin products, and polyester monomers such as TMPTA, TPGDA, HDDA, and HEA ...is one of Mega's strengths. Along with a technical team with experience and practice… Mega is always a reliable partner and accompanies you to success.
Source: Collection
>> Click HERE for the best paint chemicals on the market<<
Contact
MEGA VIETNAM
Office address: Floor 2-A2-IA20, Nam Thang Long Urban Area, Pham Van Dong Street,
Dong Ngac Ward, Bac Tu Liem District, Hanoi City, Vietnam
Email: contact@megavietnam.vn
Tel: (+84) 24 375 89089; Fax: (+84) 24 375 89 098
Website: megavietnam.vn
Hotline: 1800.577.728 Zalo: 0971.023.523





