
INTRODUCTION TO MELAMINE RESIN (AMINO RESIN)
Melamine resins are divided into three groups based on structure and properties
MOST COMMON MISTAKES WHEN APPLYING EPOXY
AUTOMOTIVE COATINGS MARKET
What's the Difference Between Polyurethane, Varnish, Shellac and Lacquer?
NO SELF-HEALING PAINT
INTRODUCTION TO MELAMINE RESIN (AMINO RESIN)
Melamine resins are divided into three groups based on structure and properties:
a. Partially etherified melamine resin, containing free methylol groups => Amino resin used for AC paint (Acid Cure).
b. Low molecular melamine resin, highly methylated, fully etherified => Amino resin used for Coil paint.
c. Relatively low molecular melamine resin, highly etherified, still contains NH groups => Amino resin used for paint drying (Baking/ Stoving).
1) Amino resin for AC paint (Acid Cure)
- Partially etherified melamine resin containing free methylol groups and residual formaldehyde. The excess formaldehyde and reaction conditions affect the molecular weight obtained. The products are mostly of relatively high molecular weight; they differ in viscosity and reactivity.
- Melamine resins react preferentially between their methylol groups and resins containing OH groups. Under the usual drying conditions of 120 and 160 °C, an acid catalyst is not necessary but can be used. If the coating formulation is for drying temperatures below 100°C, an acid catalyst (para Toluene Sulfonic Acid - pTSA) must be used. The higher molecular weight melamine resins act as a physical drying agent for the paint system.
- Melamine resins of this group contain higher amounts of free methylol groups that can undergo self-crosslinking to form dimethylene ethers. This can lead to a poorer tolerance to acids.
The plastics of this group have two disadvantages:
- First: they contain higher amounts of free formaldehyde and can form free formaldehyde during cross-linking.
- Second: due to the higher viscosity of the solution, they are not qualified to produce paints with higher solid content.
As a result, these have been widely replaced by highly etherified melamine resins containing residual NH groups (group c).
>> Get advice on technical solutions during product construction <<
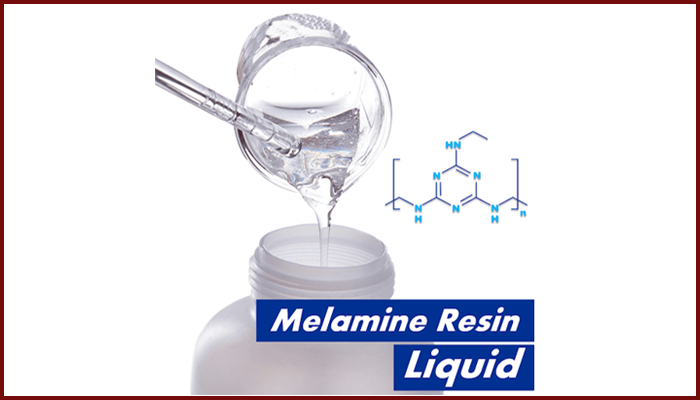 Melamine resin
Melamine resin
2) Amino resin for Coil paint:
- The best known low-molecular, highly methylated, fully etherified melamine resins are those containing methanol in the form of etherified monomeric alcohol. They are vicious or waxy liquids and are usually insoluble in water.
- Since the ether conversion reaction is the slowest of the crosslinking reactions, a relatively high drying temperature (180 to 200 °C) or catalysis is required. The preferred catalysts are acids, especially sulphonic acids, although acidic phosphoric esters or their amino salts can be used. With the optimal balance of temperature, time, and catalyst, the film formation of the paint results in cross-linked co-structures.
These paint films have the following advantages: relatively good weather resistance, flexibility, and good adhesion between coats.
However, because of their optimal solubility, the low viscosity of the resins results in paints with high solid content.
- This resin is used in industrial coatings, especially automotive paints, and for Coil paint - Can paint. In addition, there are low molecular resins that are highly etherified with butanol. They are mainly used for acid-curing paints.
3) Amino resin for paint drying
- The relatively low molecular weight melamine resin, which is highly etherified but still contains the remaining NH groups, is significantly more reactive than the fully etherified ones.
- At normal drying temperatures (120 to 160 °C), they do not need any catalyst. However, acid catalysts can also be used. The excess NH groups can react with the methylol groups to form a methylene bond, with cleavage of the monoalcohol (self-crosslinking).
- On the other hand, the directional effects exerted by this NH group on the neighboring methylol ether group increased the rate of ether conversion, and thus, crosslinking might have taken place at lower temperatures than for melamine resins. was completely etherified. The different solubility of these grades results in a higher viscosity than that of group b resins, resulting in a slightly lower solids content at the same viscosity used.
Advantages: Due to the low content of methylol, the amount of free formaldehyde is lower than other types. The relatively low amount of free formaldehyde generated during the drying and curing process is an advantage in terms of minimizing environmental pollution and toxicity to users.
Currently, Mega Vietnam General Trading Company Limited is supplying amino resin with many different types, serving many different applications, especially amino resin for drying paint. If you have any needs about Melamine resin (Amino resin), please contact us with the following information:
>> Click for the best rubber chemicals on the market today <<
Contact
MEGA VIETNAM
Office address: Floor 2-A2-IA20, Nam Thang Long Urban Area, Pham Van Dong Street,
Dong Ngac Ward, Bac Tu Liem District, Hanoi City, Vietnam
Tel: (+84) 24 375 89089; Fax: (+84) 24 375 89 098
Website: megavietnam.vn
Hotline: 1800.577.728 Zalo: 0971.023.523





